Posted in Airflow Obstruction | 07/01/2015
Acute Response Study There was no difference in bronchodilatation achieved with MDI and NEB after one ujiit dose or at FEVi plateau (Table 2). The average doqe required to achieve maximal bronchodilatation was 5.8 mg for NEB and 2.8 mg for MDI (five times the usual recommended MDI dose). The significant increase in 6MWD after maximum bronchodilatation was similar for both MDI and NEB. No patient experienced significant side effects of tremor or palpitations during this or the domiciliary study.
Read more
Posted in Airflow Obstruction | 06/01/2015
Patient Assessments Spiwmetry: Patients were assessed at the same time of day on four occasions. Beta-agonists were omitted for six hours prior to testing. The FEV, and VC were measured on a Vitalograph spirometer using the best of three measurements. In the acute response studies, assessments were made on consecutive days when baseline spirometry differed by less than 10 percent. Cumulative unit doses of terbutaline and placebo MDI and NEB were given and spirometty was recorded 10 min after each dose until FEV, plateaued. Baseline spirometry was assessed at the end of each treatment fortnight during the outpatient study. lumigan eye drops
Read more
Posted in Airflow Obstruction | 05/01/2015
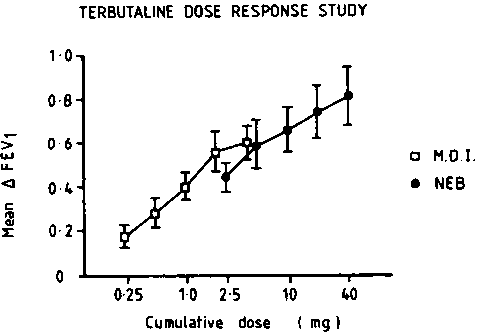
Dose Response Study Prior to the trial, the doses of terbutaline administered by MDI and NEB required to produce similar degrees of bronchodilatation were established using separate cumulative dose response curves (Fig 1). Eight of the nine asthmatic patients who went on to participate in the outpatient study were tested on two consecutive days when baseline FEV, differed by less than 10 percent. Therapy with MDI terbutaline 1.25 mg (five puffs) was found to be equipotent with NEB terbutaline 2.5 mg (0.25 ml). These doses were used in the acute response and outpatient studies.
Read more
Posted in Airflow Obstruction | 04/01/2015
Nebulized bronchodilator therapy is frequently prescribed for home use in patients with severe chronic airflow obstruction even though many of them do not have asthma and can use a hand-held device appropriately. A belief shared by many of these patients (and some physicians) is that nebulized therapy confers benefits over and above those achieved by MDI bronchodilators. Notably, patients often remark that nebulizer therapy eases sputum expectoration and provides greater relief of dyspnea. It would seem likely, however, that the impression of improved clinical response to nebulized bronchodilator medications is a reflection of the dose of bronchodilator drugs delivered to the lung rather than the mode of delivery. http://fml-eye-drops.com/
Read more
Posted in Cardiorespiratory Failure | 03/01/2015
With such a pharmacologic profile, dopexamine appears to combine the properties of dopamine and salbutamol, and is expected to have stronger vasodilating properties than dobutamine. In patients with heart failure, Bayliss et al observed that dopexamine and dobutamine had comparable effects, except for a larger increase in heart rate with dopexamine. More recently, Baumann et al observed that dopexamine produced cardiovascular effects between those produced by dobutamine and sodium nitroprusside. In experimental septic shock, we observed that systemic vascular resistance decreased more with dopexamine and that left ventricular stroke work increased more with dobutamine, consistent with a stronger inotropic effect of dobutamine but the stronger vasodilating of critically ill patients with insufficient cardiac output during an episode of acute respiratory failure. In these patients, systemic vascular resistance is not as high as may be expected in the absence of infection; thus, the vasodilating effects of dopexamine could be poorly tolerated.
Read more
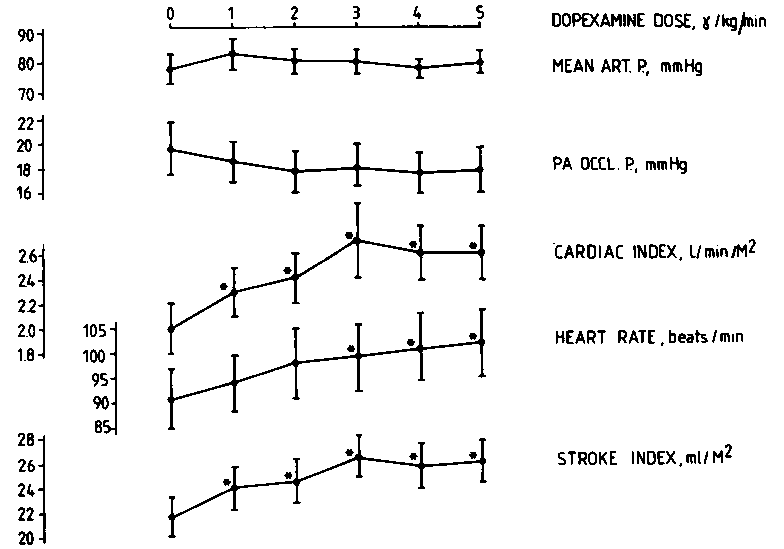
Posted in Cardiorespiratory Failure | 02/01/2015
The dopexamine administration did not significantly influence arterial pressure (Fig 1) or pulmonary arterial pressure. Pulmonary artery balloon-occluded pressure slightly decreased from 19.6±2.1 to 17.8 ± 1.7 mm Hg (change not statistically significant). Cardiac index increased significantly from 2.0 ±0.2 to 2.6 ± 0.2 L/min*m2. Accordingly, left ventricular stroke work increased from 17.3 ±1.5 to 22.1 ±2.4 g*m2 (p<0.01) and systemic vascular resistance index decreased from 3,792 ±1,035 to 2,194 ±823 dynes’s’cm^m2 (p<0.01). The increase in cardiac output was in part due to a dose-related increase in heart rate from 91 ±6 to 102 ±7 beats/min (Fig 1). However, no significant arrhythmia was observed. The increase of the infusion rate above 3jJig/kg/inin was not clearly beneficial, as only a further increase in heart rate was observed (Fig 1). pilocarpine eye drops
Read more

Posted in Cardiorespiratory Failure | 01/01/2015
Dopexamine hydrochloride is a new synthetic catecholamine that has β2-agonist and dopaminergic activities but only weak fVagonist activity and no a-agonist activity. The drug also inhibits the active reuptake of neuronally released norepinephrine (up-take-1). Dopexamine has been shown to exert strong vasodilating effects and also to improve various indexes of myocardial contractility” without significantly altering myocardial oxygen balance. Hence, the combination of inotropic, afterload-reducing and renal vasodilating effects can be useful in the management of heart failure. travoprosteyedrops.com
Read more





