The Effect of Intravenous Amiodarone on Heart Rate in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction or Ischemia and Sinus Tachycardia: Results
 Patients’ Characteristics
Patients’ Characteristics
There were 22 patients (Table 1), 11 men and 11 women, with a mean age of 63.5 years (range 48 to 83 years). Eighteen patients presented with acute myocardial infarction, which was of anterior location in 15 patients and of inferior location in three. Four patients presented with acute myocardial ischemia which was anterior in three and inferior in the remaining patient.
Efficacy of Intravenous Amiodarone
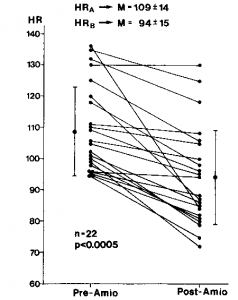
Prior to amiodarone administration the sinus heart rates ranged from 95 to 136 beats/min (mean 109 ± 14 beats/min). Following the administration of amiodarone, the sinus rates slowed in all but two patients to 72 to 125 beats/min (mean 94 ± 15; p<0.0005) (Fig 1).
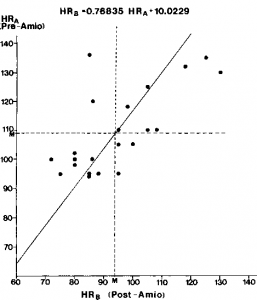
No patient demonstrated an increase in heart rate. There was a linear correlation between the initial heart rate, before drug administration, and the final heart rate, after amiodarone was given (r = 0.6930; p<0.0005) (Fig 2). In addition, as shown in Figure 2, most of the patients (eight of ten) who had heart rates higher than the mean before amiodarone administration maintained a relatively high heart rate (above the mean) after drug administration, although lower than the initial rate (right upper quadrant). A similar relationship was demonstrated between the lower initial heart rates and the final ones, which also remained lower than the mean in most of these patients (nine of 12; left lower quadrant).
Efficacy of Amiodarone in Different Hemodynamic Subsets
There were 14 patients in Killip class 1. Amiodarone slowed their heart rate from a mean of 105 ± 10 to a mean of 88±11 beats/min, p<0.01. Seven of these patients slowed their heart rate 20 or more beats/min from a mean of 109 beats/min to 85 beats/min. Four patients slowed their heart rates from 10 to 20 beats/ min (mean of 97 to 83 beats/min). The remaining three patients slowed their heart rates by 2, 5, and 7 beats/ min, respectively.
There were five patients in Killip class 2. Amiodarone slowed their heart rate from a mean of 118 ± 14 to a mean of 81 ±39 beats/min (p = NS). One patient had slowing of more than 20 beats/min (from 136 to 85 beats/min), and three patients from 10 to 20 beats/min (mean of 116 to 103 beats/min). The remaining patient had heart rate slowing of 5 beats/min. There were three patients in Killip class 3 to 4, one with slowing of 10 beats/min (from 135 to 125 beats/min). In the remaining two patients there was no change in heart rate.
Side Effects of Amiodarone Administration
Most of the patients had a mild, asymptomatic reduction in blood pressure (Table 1). One patient in cardiogenic shock decreased her systolic blood pressure from 90 to 70 mm Hg. The same patient developed transient first-degree Ml block (PR = 0.32 s) after drug administration. Except for this patient, no hemodynamic deterioration was observed during administration of amiodarone. Four patients were monitored with a Swan-Ganz catheter (including two patients in Killip class 3 to 4), and no changes in the pulmonary artery capillary pressure were observed.
Table 1—Clinical Characteristics and Response to Amiodarone
| Sex Age, Yr | Disease | Site | KC | Before Amio | After Amio | ||
| Rate | BP | Rate | BP | ||||
| l/M/61 | MI | Ant | I | 95 | 110/95 | 88 | 110/70 |
| 2/F/57 | MI | Ant | I | 118 | 95/70 | 98 | 95/70 |
| 3/F/69 | MI | Ant | I | 98 | 100/60 | 80 | 95/60 |
| 4/M/83 | Iseh | Ant | I | 120 | 140/80 | 86 | 130/80 |
| 5/F/41 | MI | Ant | II | 110 | 115/80 | 95 | 110/80 |
| 6/F/71 | MI | Inf | I | 100 | 110/70 | 80 | 110/70 |
| 7/M/63 | MI | Ant | I | 125 | 120/70 | 105 | 120/70 |
| 8/F/50 | MI | Inf | I | 110 | 100/60 | 108 | 90/60 |
| 9/F/69 | MI | Ant | II | 105 | 130/90 | 100 | 110/85 |
| 10/F/74 | MI | Ant | II | 136 | 100/60 | 85 | 100/60 |
| ll/F/73 | MI | Ant | IV | 130 | 90/60 | 130 | 80/60 |
| 12/M/76 | MI | Ant | I | 95 | 110/80 | 75 | 110/80 |
| 13/M/53 | Iseh | Inf | I | 100 | 140/90 | 72 | 140/90 |
| 14/M/58 | MI | Ant | III | 95 | 90/60 | 95 | 90/60 |
| 15/M/68 | Iseh | Ant | I | 95 | 120/70 | 82 | 120/70 |
| 16/F/63 | MI | Ant | II | 105 | 110/60 | 95 | 110/60 |
| 17/M/72 | MI | Ant | I | 100 | 105/70 | 86 | 105/70 |
| 18/M/56 | MI | Ant | I | 102 | 100/70 | 80 | 100/70 |
| 19/F/64 | MI | Ant | IV | 135 | 90/60 | 125 | 70/50 |
| 20/M/66 | MI | Inf | I | 110 | 130/90 | 105 | 120/80 |
| 21/M/48 | MI | Ant | II | 132 | 110/70 | 118 | 110/70 |
| 22/F/63 | Iseh | Ant | I | 95 | 120/80 | 85 | 120/80 |
Figure 1. Effect of intravenous amiodarone (amio) on heart rate (HR). There is a significant slowing, from 109 ± 14 to 94 ± 15 beats/ min (p<0.0005).
Figure 2. Simple linear regression showing a linear correlation between the initial heart rate (preamiodarone) and the final heart rate (postamiodarone) (r = 0.6930; p<0.005).
Category: Myocardial Infarction
Tags: heart rate, Ischemia, myocardial infarction, sinus tachycardia