
Posted in Health | 11/10/2009
SBP is a major problem encountered in patients with liver cirrhosis, with an incidence of 5-30% of all infections, and hospital mortality constitutes about 50% of all SBP cases. Obviously, a positive bacteriological culture of ascitic fluid is the “gold standard” and prerequisite for the diagnosis of SBP. The value of ascitic leukocyte count has been studied in detail and is still accepted as a “silver standard” diagnostic criterion for SBP.
Read more
Posted in Health | 10/10/2009
Biochemical examinations of the serum and ascitic fluid were summarized in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. On evaluation of these parameters, cholesterol, lactate dehydrogenase, total protein, albumin and globulin levels in the ascitic fluid were higher in group 3 than group 2. Serum lactate dehydrogenase level was higher in group 3 than group 1. Triglyceride levels in the ascitic fluid and serum in group 3 was higher when compared with group 1 and group 2. There was no statistically significant difference in the rest of the parameters (Tables 1 and 2).
Read more
Posted in Health | 09/10/2009
A total of 92 patients with ascites were evaluated. Biochemical and hematological investigations besides microbiological culture of the ascitic fluid were routinely done to all of the patients. Complete blood count, biochemical investigations, abdominal ultrasonography and cytologic examination of the ascitic fluid were performed. Ninety-two patients were divided to three groups according to etiology of the ascitic fluid:
Read more

Posted in Health | 08/10/2009
INTRODUCTION C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute phase 6-globulin. While the precise in vivo functions of CRP during the inflammation state is not known, there is considerable evidence indicating a role in the recognition and elimination of foreign pathogens as well as potentially toxic endogenous substances released from damaged tissue by assisting humoral and cellular immunity. CRP, as a acute phase reactant, binds to different substrates. It activates the complement system, takes part in cytokine secretion and increases the phagocytosis of leukocytes.
Read more

Posted in Health | 05/10/2009
CDllb and CD 18 are members of the integrin family of adhesion molecules, which consist of transmembrane glycoproteins expressed primarily on neutrophils and monocytes. They form heterodimer complexes from the noncovalent union of the alpha and beta subunits before being transported to the cell sur face. In this regard, the CD 18 (beta2) integrin combines with three distinct alpha chains, namely CDl la, CDl lb or CDl lc. The association of CDl lb and CD 18 forms the complement receptor, CR3 (or MAC-1) heterodimer, which participates in complement binding, phagocytosis and intercellular adhesion. The sequence of this neutrophil-endothelial binding has recently been studied carefully. After an inflammatory stimulus, neutrophils roll along the postcapillary venules at velocities distinctly below that of flowing blood. After some rolling, the cells stop, change shape and extravasate into extravascular tissue. The initial capture of the traveling neutrophils is mediated through the expression of another family…
Read more
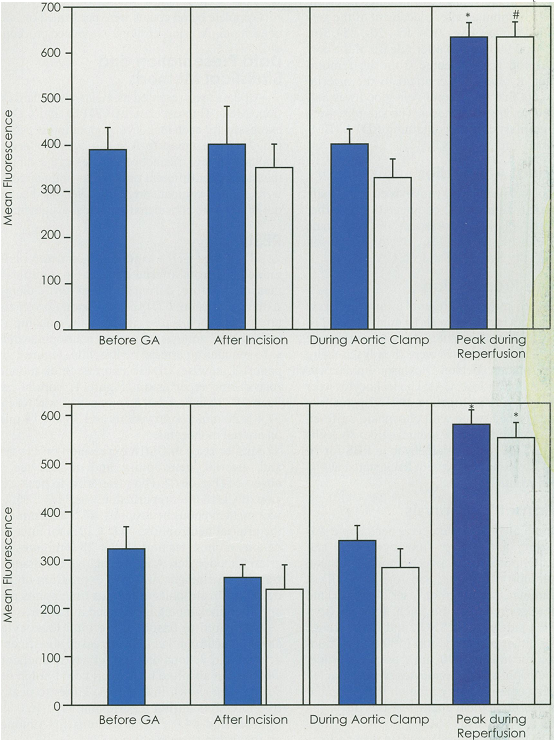
Posted in Health | 04/10/2009
CDl lb and CD 18 expressions on neutrophils and monocytes from arterial and venous samples were measured before, during and after aortic clamping. After reperfusion, CDl lb expression on venous and arterial neutrophils rose significantly, reaching a peak at 34.4 ± 27 minutes on venous neutrophils and 38.5 ±16 minutes on arterial neutrophils (Figure 1, upper panel). Likewise, CDl lb expression on monocytes rose during reperfusion (Figure 1, bottom panel). Peak CDl lb expression on monocytes was reached at 31.4 ± 20 minutes on venous and 36.4 ± 14 minutes on arterial monocytes.
Read more
Posted in Health | 03/10/2009
Institutional human subjects committee approval and individual informed consent were obtained prior to the study. Eight Caucasian male patients aged 55-81 with past history of hypertension, tobacco smoking and arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease undergoing elective infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm repair were studied. Radial artery and pul- induction of general anesthesia, a right femoral vein monary artery catheters were placed prior to induecatheter was placed. Each patient received 80-100 tion of general endotracheal anesthesia. After the units per kilogram of heparin intravenously 10 minutes before application of the aortic clamp. Mean aortic cross-clamp time was 85 minutes (range 47-130 minutes), and mean duration of surgery was 241 minutes (range 150-315 minutes). There were no intraoperative complications.
Read more



